System Design Basics
Key Characteristics of Distributed Systems
Scalability
Definition: The capability to grow and manage increased demand, such as increased data volume, number of transactions.
Reliability
Definition: The probability a system will fail in a given period.
Availability
Definition: The time a system remains operational to perform its required function in a specific period.
Efficiency
Definition:
The response time(latency) means the delay to obtain the first item.
The throughput(bandwidth) number of items delivered in a given time unit (e.g., a second)
Manageability or Serviceability
How easy it is to operate and maintain.
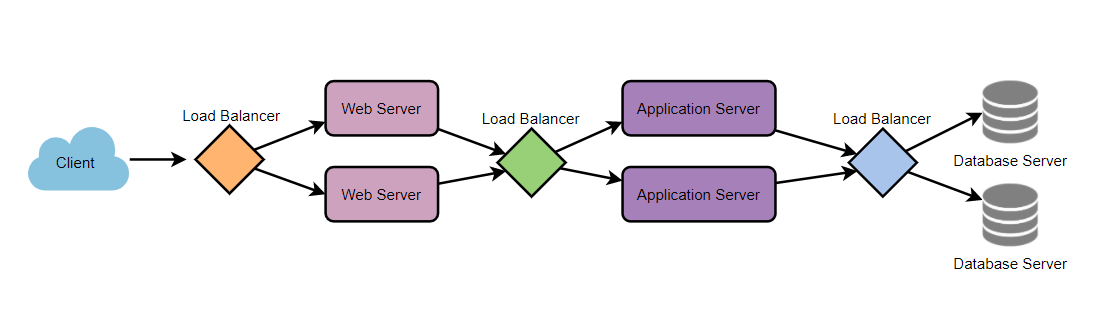
Load Balancing(LB)
Between the user and the web server
Between web servers and an internal platform layer, like application servers or cache servers
Between internal platform layers and database.
Redundant Load Balancers
Caching
recently requested data is likely to be requested again
- Application server cache
- Content Delivery Network(CDN) for static media.
- Cache Invalidation
- Write-through
- Write-around
- Write-back
- Cache eviction
- First In First Out (FIFO)
- Last In First Out (LIFO)
- Least Recently Used (LRU)
- Most Recently Used (MRU)
- Least Frequently Used (LFU)
- Random Replacement (RR)
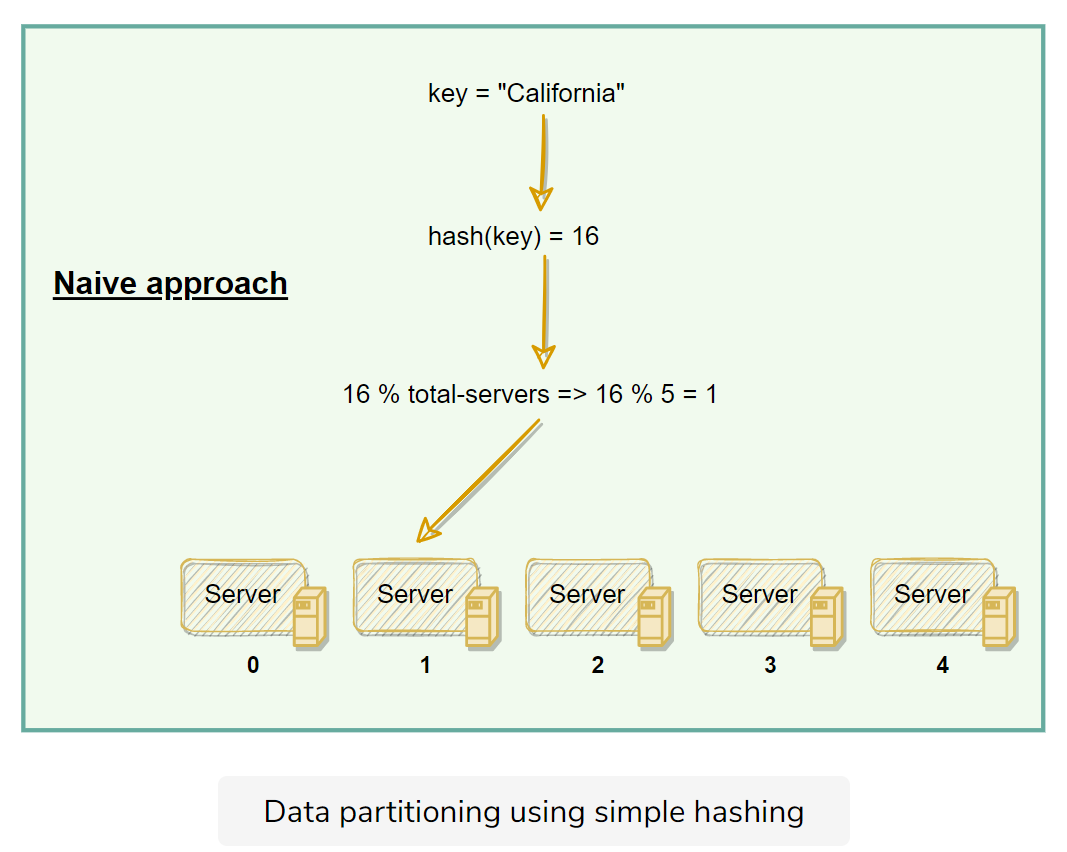
Data Partitioning
Definition: a technique to break a big database (DB) into many smaller parts
Partition Methods
- Horizontal Partitioning. (Data Sharding) Different rows in different tables. Range-based partitioning. It may lead unbalanced servers.
- Vertical Partitioning. Store tables related to a specific feature in their own server.
- Directory-Based Partitioning: create a lookup service that knows your current partitioning scheme and abstracts it away from the DB access code
Partitioning Criteria
- Key or Hash-based Partitioning: apply hash function to the entity's attribute, get partition number.
- List Partitioning: each partition has a list of values.
- Round-robin partitioning
- Composite Partitioning
Common Problems of Data Partitioning
- Joins and Denormalization
- Referential integrity
- Rebalancing
Indexes (DB)
Make it faster to search through the table, created one or more columns of a database table.
A Library catalog
Book name or book title sorted catalog
It decreases write performance
Adding indexes is to improve search queries performances.
Proxies
Definition: an intermediate piece of software or hardware sits between the client and the server.
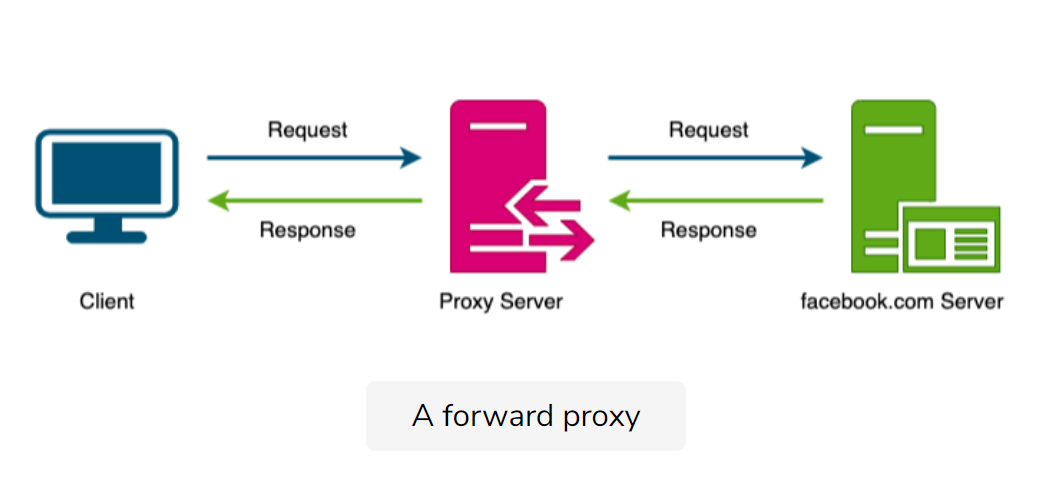
Forward proxies
-
cache data
-
filter requests
-
log requests
-
transform requests
-
collapsed forwarding to combine the same data access requests into one request.
Reverse proxy
Definition: the node retrieves resources from one or more servers on behalf of a client.
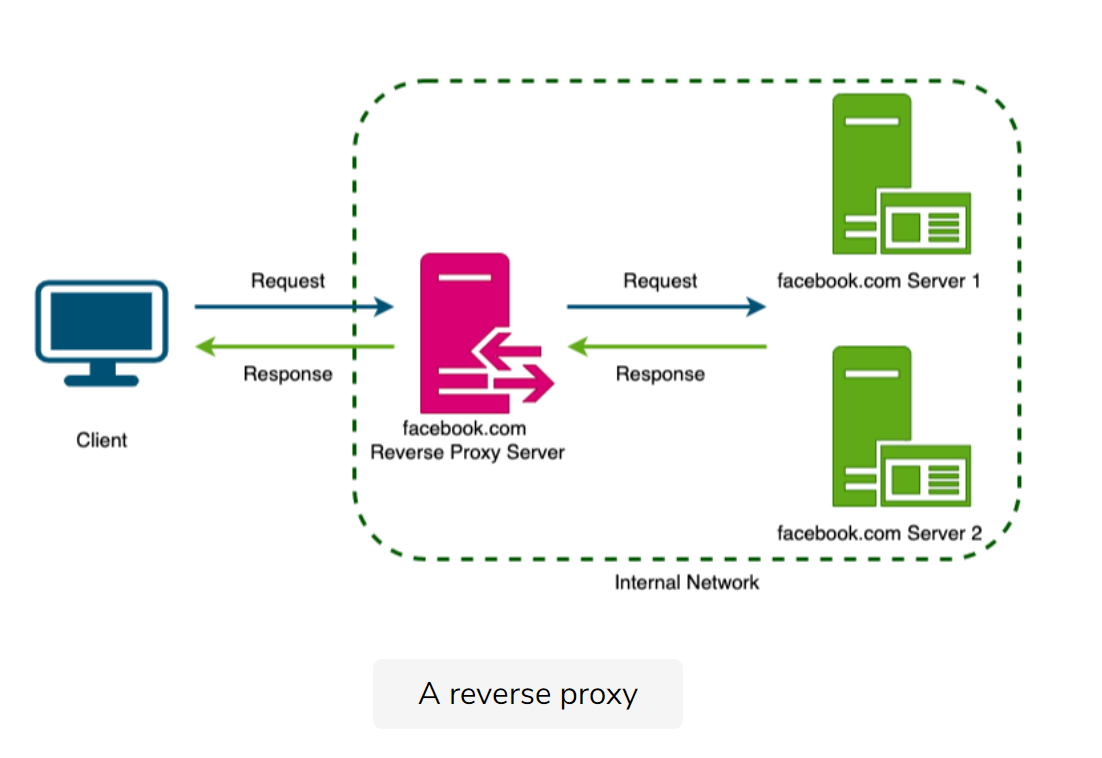
- caching
- load balancing
- anonymizing the servers
- routing requests to the appropriate servers
Redundancy and Replication
Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions to increase system's reliability, a form of a backup or fail-safe or performance improving.
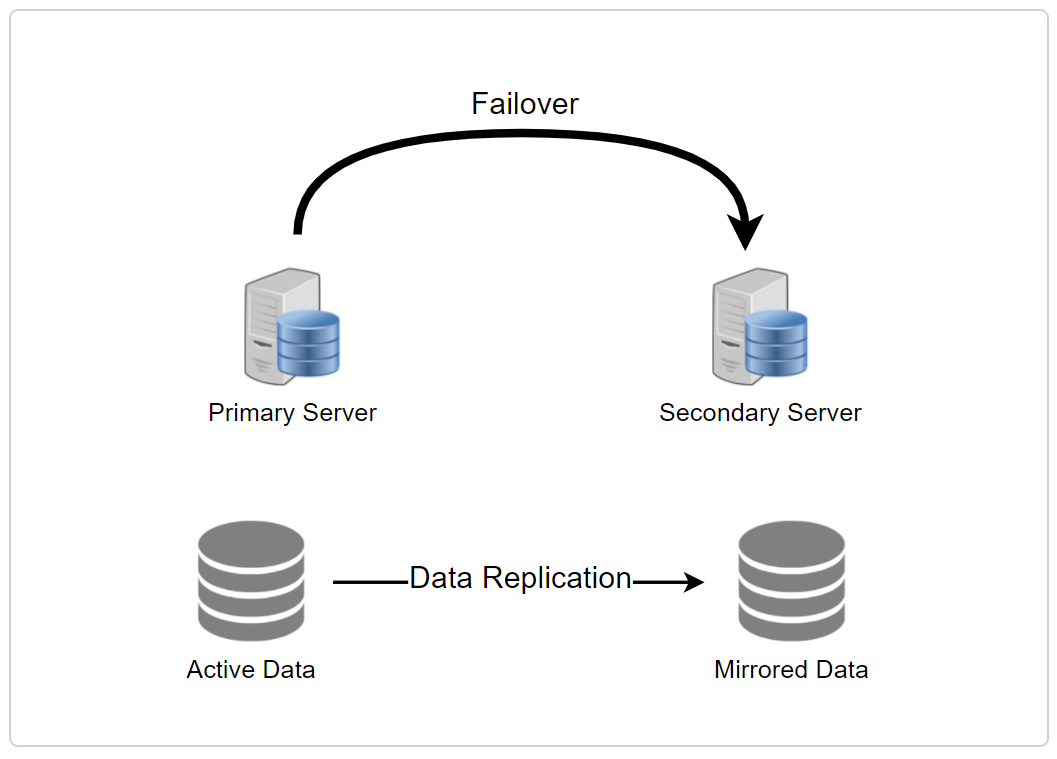
Replication means sharing information to ensure consistency between redundant resources, to improve reliability, fault tolerance or accessibility.
Widely used in DBMS, usually primary-replica relationship.
SQL vs NoSQL
SQL
Store data in rows and columns in predefined tables.
No-SQL
- Key-Value Stores: store data in key-value pairs. Redis, Voldemort, and Dynamo
- Document DB: store data in documents. CouchDB and MongoDB
- Wide-Column Databases: Instead of 'tables', column families which are containers of rows. Each rows doesn't have to have the same number of columns. Columnar databases are for large datasets. Cassandra and HBase.
- Graph Databases store data whose relationship are in a graph, store the data in nodes, properties, and lines. e.g. Neo4J and InfiniteGraph.
Differences
| SQL | No-SQL | |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | tables | key-value, document, graph, or columnar |
| Schema | Fixed schema | dynamic, add in the fly |
| Querying | structured query language | UnQL (Unstructured Query Language) |
| Scalability | Vertically | horizontally |
| ACID Compliancy | ACID compliant | sacrifice ACID compliance for performance and scalability |
Consistent Hashing (New)
Data replication
A carefully designed scheme for partitioning and replicating the data enhances the performance, availability, and reliability of the system
David Karger et al. first introduced Consistent Hashing in their 1997 paper
Consistent Hashing maps data to physical nodes and ensures that only a small set of keys move when servers are added or removed.
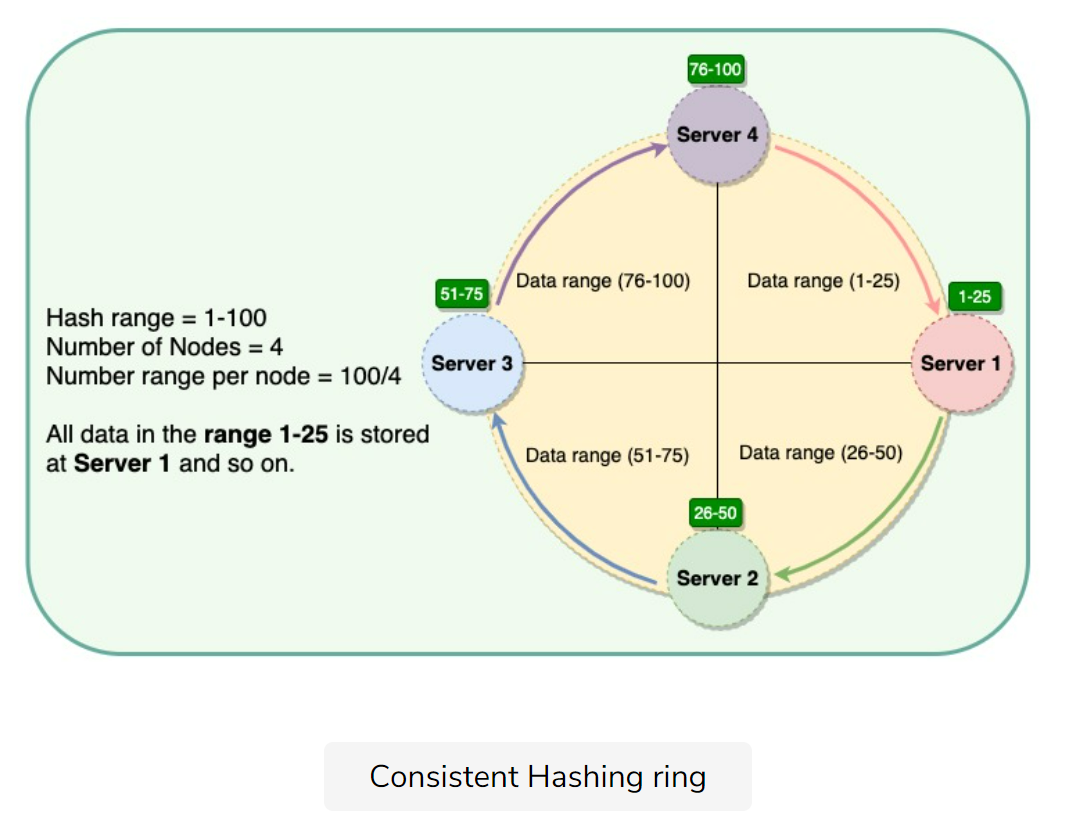
Each node is assigned one of these ranges. The start of the range is called a token.
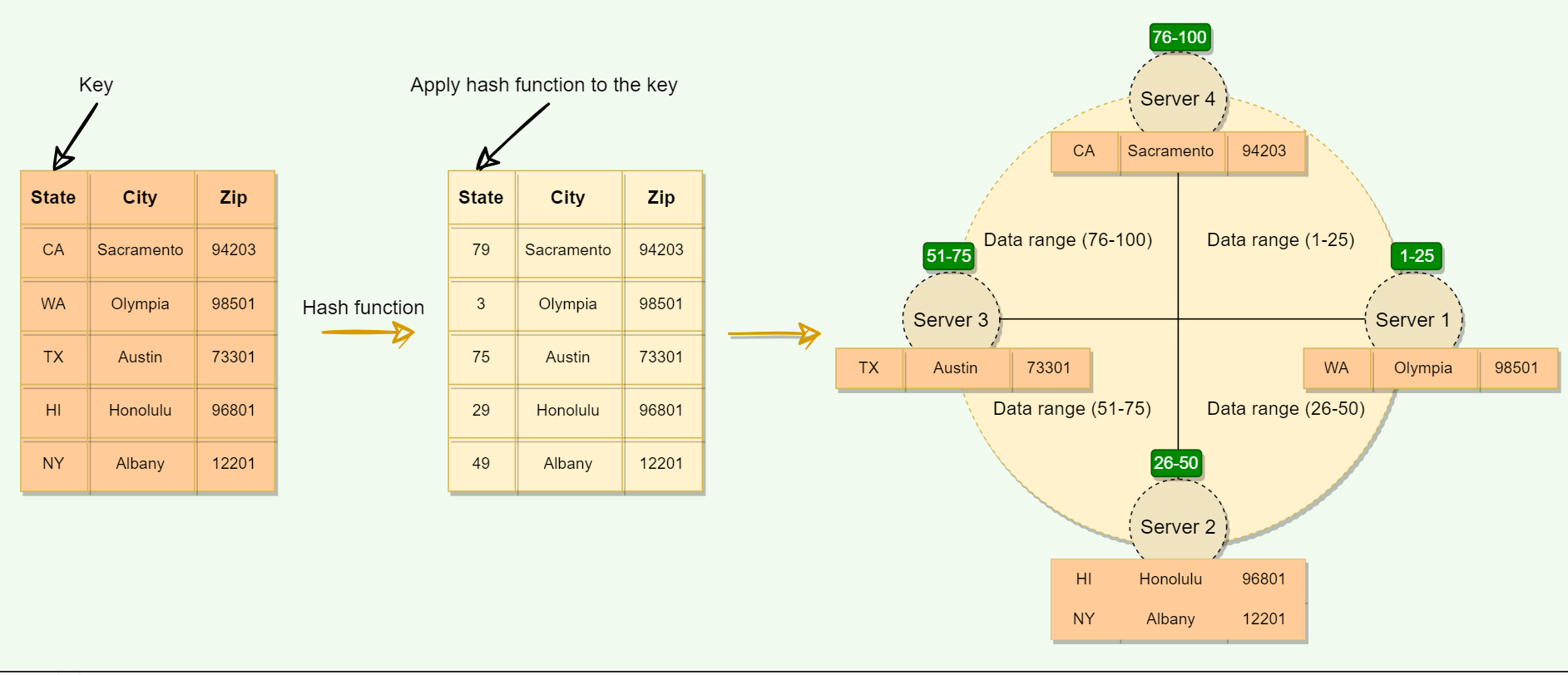
However, the above scheme may result in non-uniform data and load distribution.
Virtual nodes
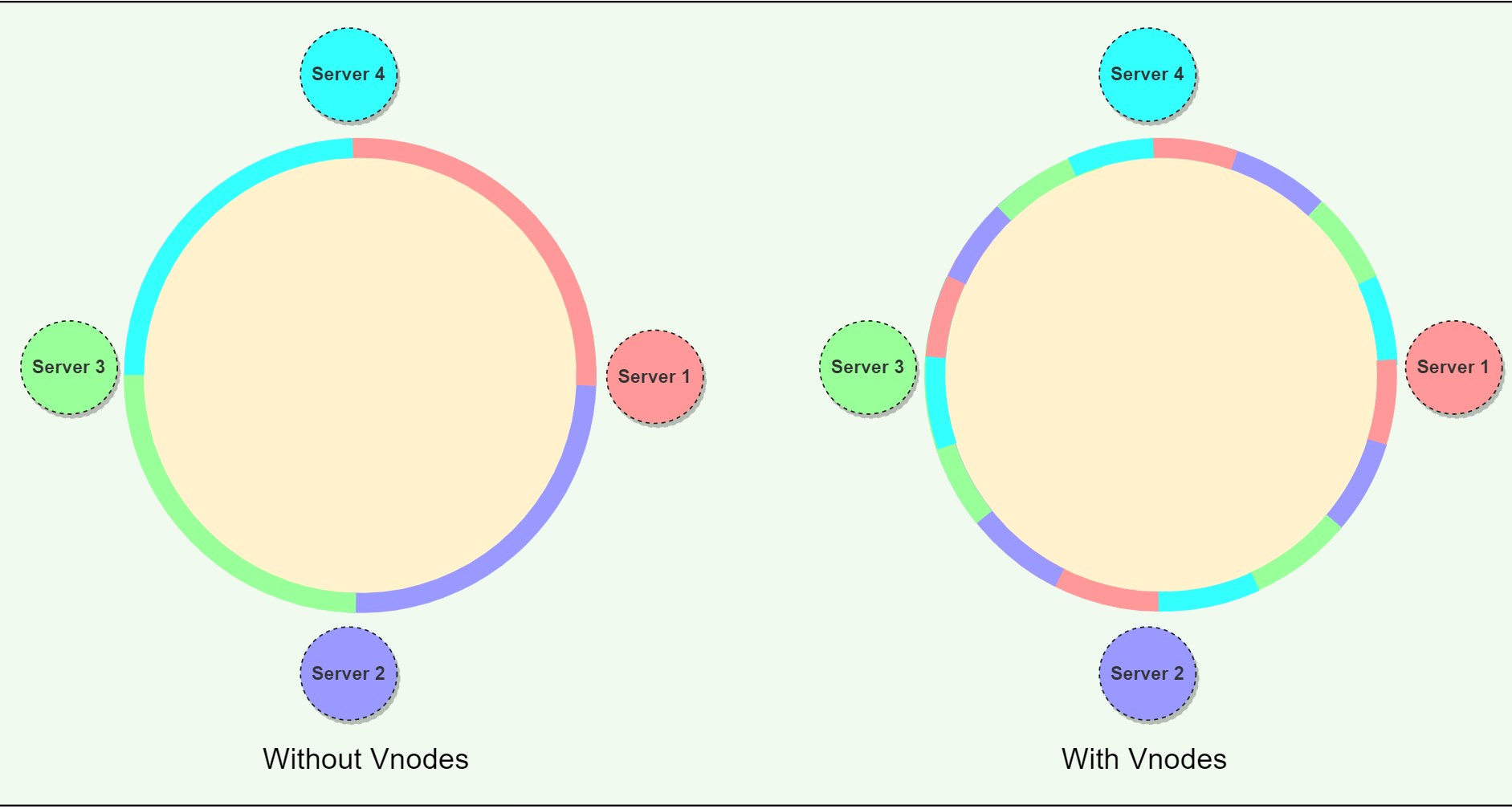
Mapping Vnodes to physical nodes on a Consistent Hashing ring
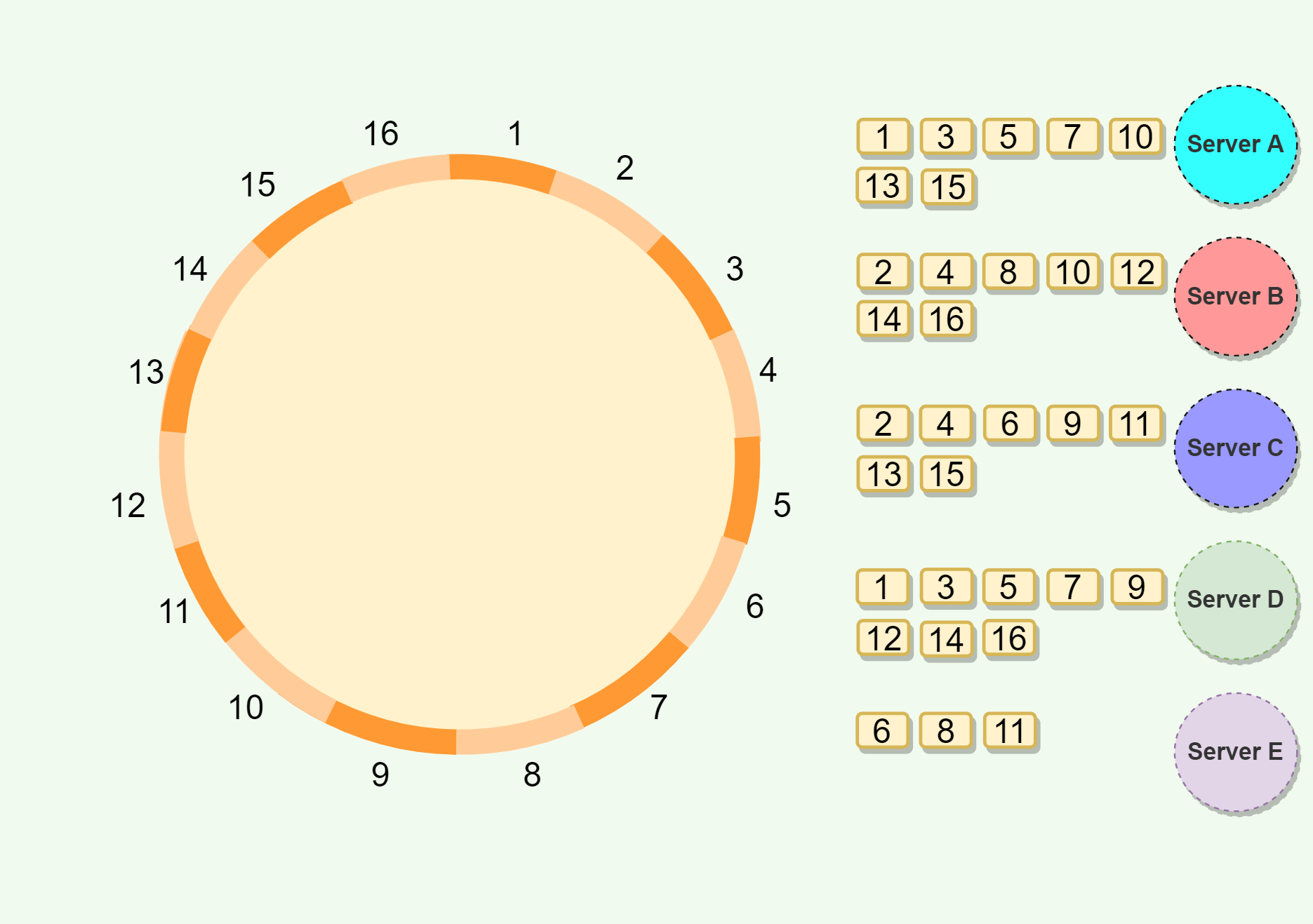
Mapping Vnodes to physical nodes on a Consistent Hashing ring
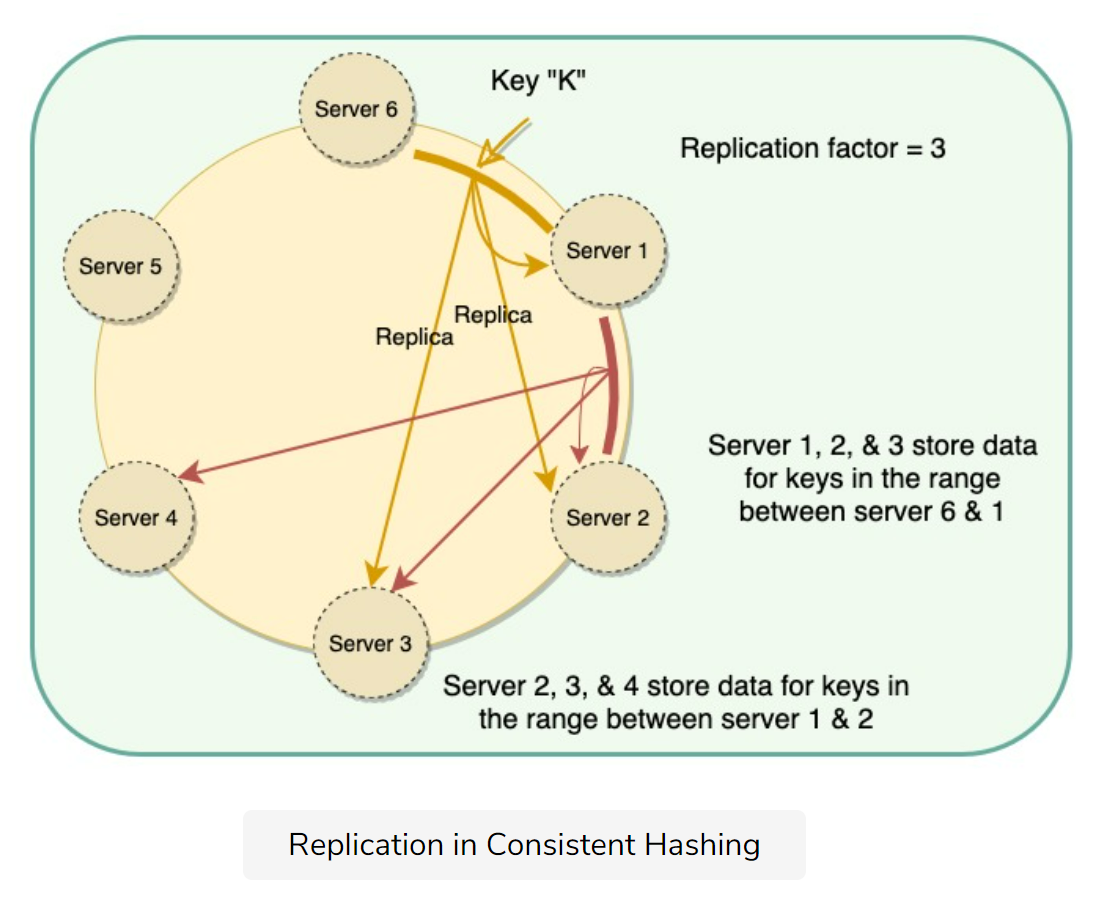
Replication in Consistent Hashing
Use cases
Amazon’s Dynamo
Apache Cassandra
Long-Polling vs WebSockets vs Server-Sent Events
Ajax Polling
The basic idea is that the client repeatedly polls (or requests) a server for data.
HTTP Long-Polling
With Long-Polling, the client requests information from the server exactly as in normal polling, but with the expectation that the server may not respond immediately
WebSockets
WebSocket provides Full duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection
Server-Sent Events (SSEs)
Under SSEs the client establishes a persistent and long-term connection with the server.
cases:
- Real-time traffic from the server to the client.
- the server is generating data in a loop and will be sending multiple events