System Design Patterns
Bloom Filters
The Bloom filter data structure tells whether an element may be in a set, or definitely is not.
e.g. BigTable (and Cassandra), any read operation has to read from all SSTables that make up a Tablet.
Consistent Hashing (HA)
The act of distributing data across a set of nodes is called data partitioning.
Consistent Hashing maps data to physical nodes and ensures that only a small set of keys move when servers are added or removed.
Each notes is assigned several smaller hash ranges, where each range is considered a Vnode.
Dynamo and Cassandra use Consistent Hashing to distribute their data across nodes.
Data Consistency
Quorum - Consistency
In a distributed environment, a quorum is the minimum number of servers on which a distributed operation needs to be performed successfully before declaring the operation’s overall success.
Quorum is to ensure strong consistency
Leader and Follower
The leader is responsible for data replication and to coordinate work.
e.g. Kafka, each partition's leader read, write into that partition and replicate it's data into backup partition.
Controller(broker) admin operations, creating, deleting topics, add partitions, check health of other brokers.
Write-ahead Log(WAL) (append-only log)
or Transaction log or commit log
Write the log into a log file before system processing.
Each log should contain enough information to redo or undo.
Each log has an identifier which helps process log segmentation/log purging.
e.g. Cassandra receive a write request, write the data to a commit log first. write to the commit log before write data to a MemTable.
Kafka implements a distributed commit log to persistently store all messages.
Chubby: all DB transaction are stored in a transation log.
Segmented Log
Break down the log into equal-sized log smaller segments. (every 4 hours or every 1GB)
e.g. Cassandra: commit log segments are truncated when it flushed data to SSTables.
Kafka: use log segmentation to implement storage for it's partion.
High-Water mark
The high water mark index is the last log index replicated to a quorum of followers.
e.g. Kafka brokers keep high-water mark where consumers can only see the messages until this mark.
Communication
Lease
Clients get time-bound lease on resources to avoid crash, deadlock, lock indefinitely.
e.g. Chubby clients maintain a time-bound session lease with the leader.
Heartbeat
Each server periodically sends a heartbeat message to a central monitoring server to indicate it's still alive.
e.g.
GFS leader communicates with ChunkServer in headbeat messages for instructions and states.
HDFS: NameNode keeps track of DataNodes through a heartbeat mechanism.
Gossip Protocol
Each node keeps track of other states' state information and gossip its known servers' information to random node every second.
e.g.
Dynamo & Cassandra uses this gossip protocol across nodes.
Detecting failures
Detecting node Failures, restart, network issues, etc.
Phi Accrual Failure Detection
Use adaptive failure detection algorithm to calculate a suspicion level about a server.
It uses historical heartbeat information to make the threshold adaptive.
e.g. Cassandra uses it.
Split-brain
The common scenario in which a distributed system has two or more active leaders is called split-brain
Split-brain is solved through the use of Generation Clock, monotonically increasing number to indicate a server's generation.
e.g.
Kafka uses "Epoch number".
HDFS put epoch number as part of transaction ID for NameNode's generation.
Cassandra uses generation number to distinguish a node's state before and after a restart.
If the generation nubmer in the gossip message is higher, it knows that node was restarted.
Fencing
Put a "fence" around the previous leader.
- Resource fencing. revoke its access to the shared storage directory or disable its network port.
- Node fencing. Power off or reset the node. "Shoot the other node in the head"(STONIT)
Data integrity
Checksum
Use a cryptographic hash function like MD5, SHA-512 to calculate checksum.
Commands: md5sum, sha512sum
Vector Clocks
Use vector clocks - (node, counter) pairs.
First object's clock < all nodes in the second clock. Abandon the first object. Otherwise, need to have reconciliation.
e.g.
Amazon’s Dynamo uses Vector Clocks.
Distributed system Theorems
CAP Theorem
- Consistency
- Availability
- Partition tolerance.
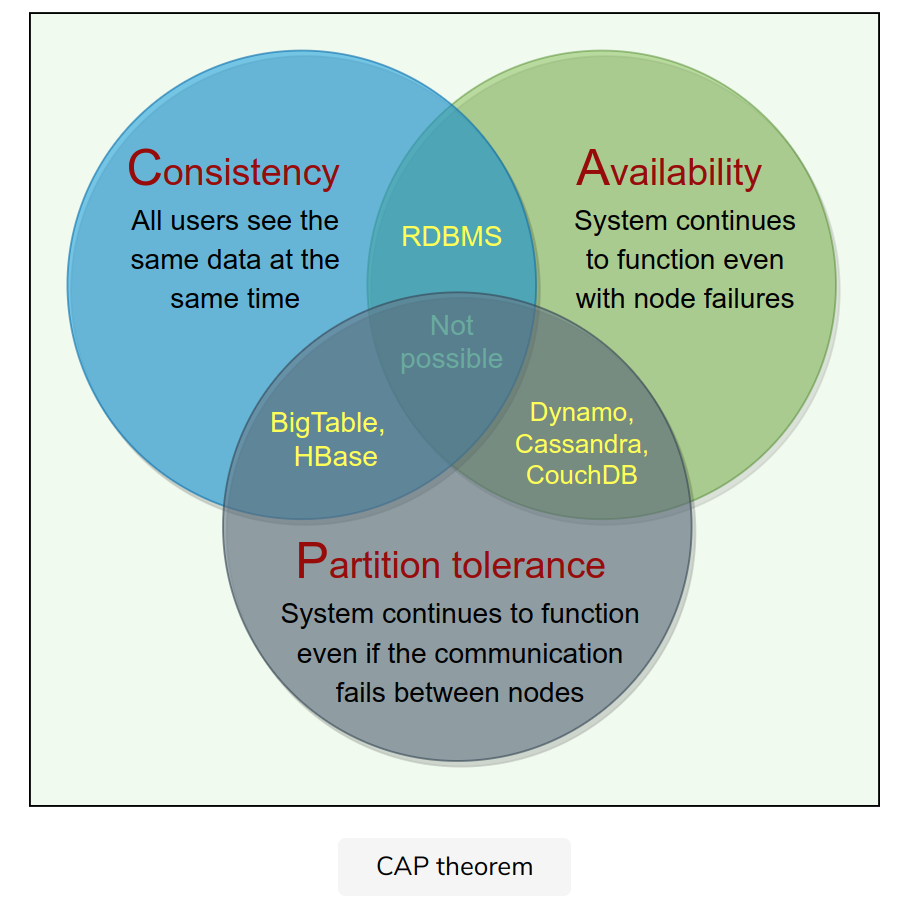
e.g. Dynamo: In CAP theorem terms, Dynamo falls within the category of AP systems and is designed for high availability at the expense of strong consistency.
BigTable: CP system. it has strictly consistent reads and writes.
PACELEC Theorem
ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) databases chose consistency
e.g. RDBMSs like MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server (refuse response if it cannot check with peers)
BASE (Basically Available, Soft-state, Eventually consistent) databases chose availability
e.g. NoSQL databases like MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis (respond with local data without ensuring it is the latest with its peers).
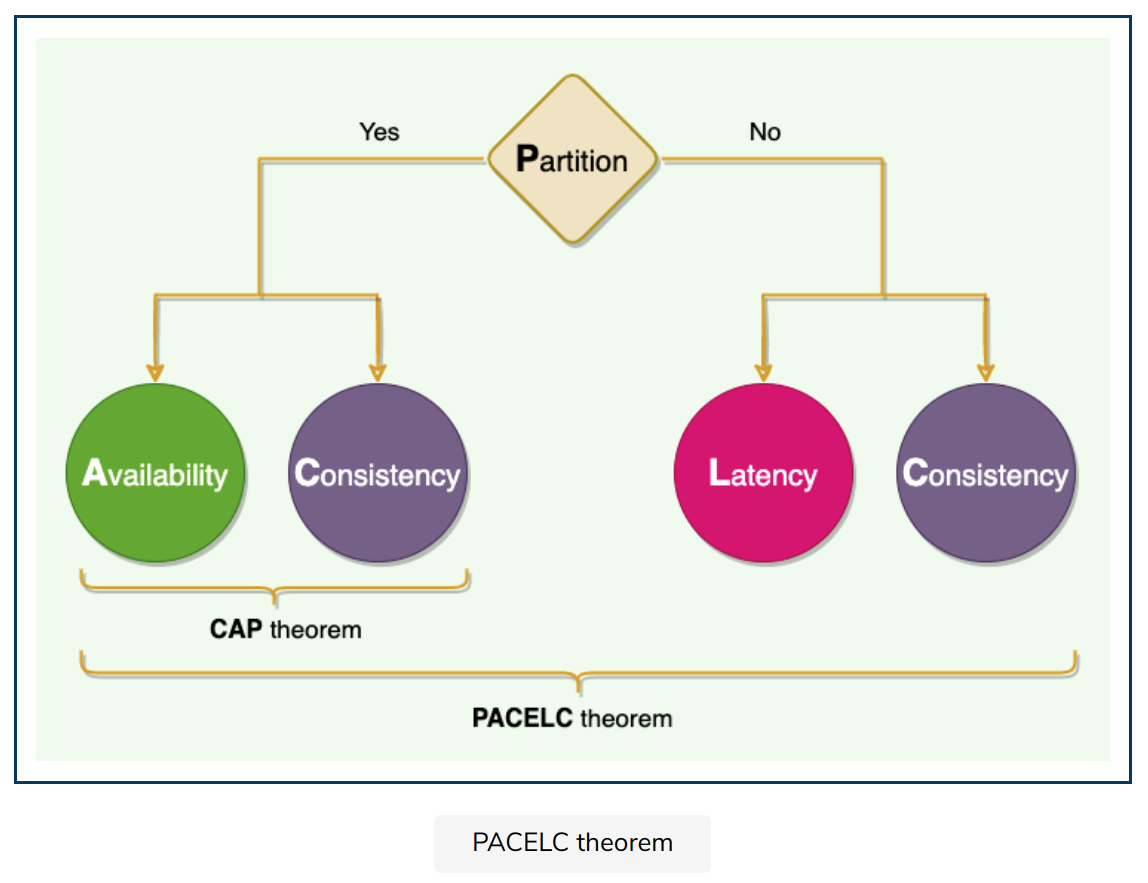
Dynamo and Cassandra are PA/EL systems
BigTable and HBase are PC/EC systems
MongoDB can be considered PA/EC
Nodes Repair (Data consistency)
Hinted Handoff - Write repair
For down nodes, the system keep all missing write requests as notes(hints). Once they recover, the hints will be forwarded.
e.g. Cassandra and Dynamo uses Hinted Handoff.
Read Repair
If we read data and find stale data, then call read repair operation to push newer version.
e.g. Cassandra and Dynamo use ‘Read Repair’
Merkle/Hash Trees
How to compare a range of data on two different replicas?
e.g. Dynamo uses it.
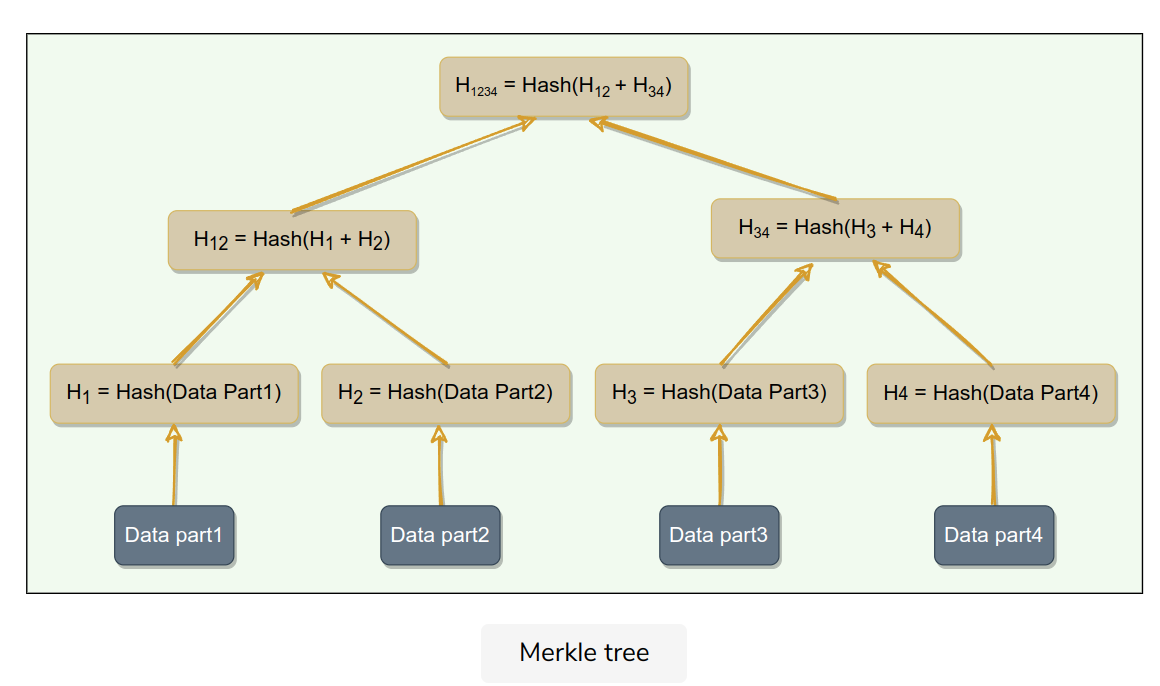
Comparing Merkle trees is conceptually simple:
- Compare the root hashes of both trees.
- If they are equal, stop.
- Recurse on the left and right children.