Database
Date type
Structured data - normalized fasion
normalized data means a unique entity occurs in only one place/table, in its simplest and atomic form and is not spread throughout the database.
Unstractured Data
User state
Relational DB
Transactions & Data Consistency
ACID – Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability.
Storing Relationships
Relational databases are built to store relationships.
Facebook as the main user-facing database.
MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Amazon Aurora, Google Cloud SQL
NoSQL Databases
JSON-based databases for frequency read & writes, typically required in social applications like Twitter, LIVE real-time sports apps, online massive multi-player games etc.
Why no-sql needed from relational DB?
Scalability
Scaling SQL databases is something which is not trivial. They have to be Sharded or Replicated to make them run smoothly on a cluster
NoSQL databases have the ability to add new server nodes on the fly & continue the work,
Clustering
the server nodes even have self-healing capabilities.
Features
Pro
Gentle Learning Curve
Schemaless
Cons
Inconsistency
No ACID
MongoDB, Redis, Neo4J, Cassandra, Google Cloud Datastore
When to use?
Handling A Large Number Of Read Write Operations
Since they have the ability to add nodes on the fly, they can handle more concurrent traffic & big amount of data with minimal latency.
Flexibility With Data Modeling
Eventual Consistency Over Strong Consistency
Running Data Analytics
Database use cases
Time-Series databases, *
Wide-Column* - Cassandra or HBase,
Document Oriented - ElasticSearch
Key-value store - Redis or Memchache
Is NoSQL more performant?
MongoDB, ExpressJS, AngularJS/ReactJS, NodeJs pick NoSQL DB.
Facebook uses MySQL for storing its social graph of millions of users.
Quora uses MySQL by partitioning the data at the application level
Polyglot Persistence to use both SQL and NoSQL
Facebook case study:
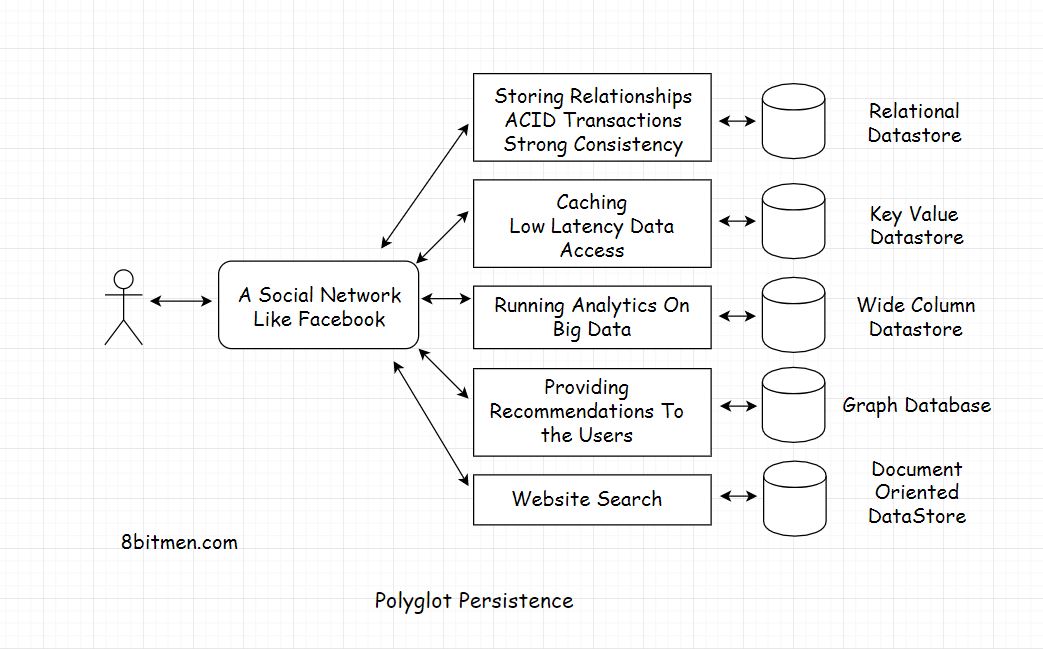
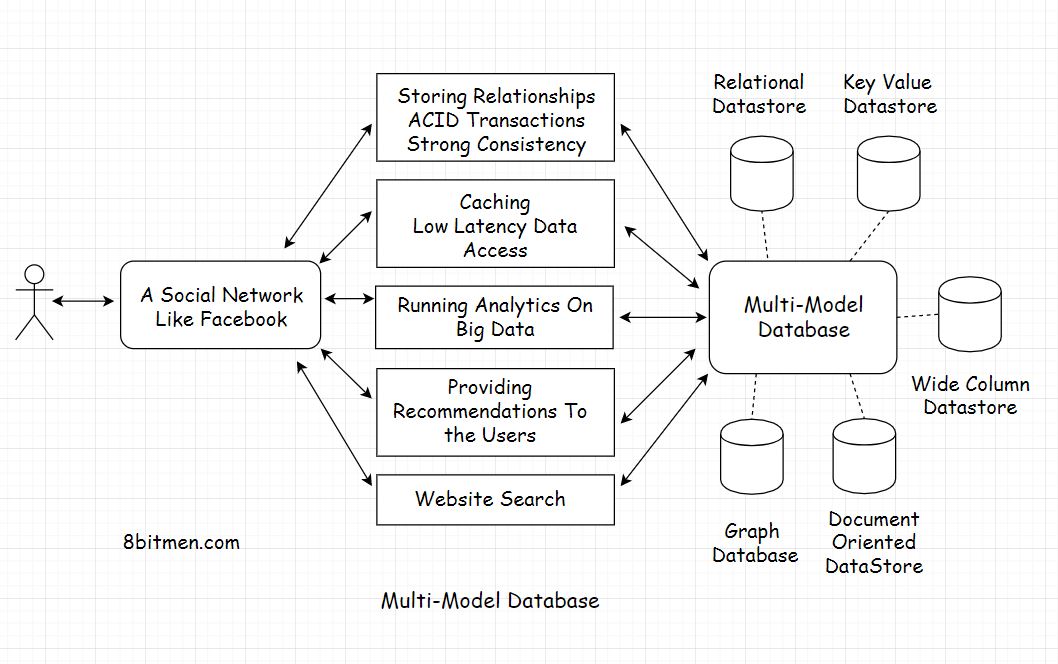
Multi-Model Databases
DB supports Graph, Document-Oriented, Relational
e.g.
Arango DB, Cosmos DB, Orient DB, Couchbase
Eventual consistency
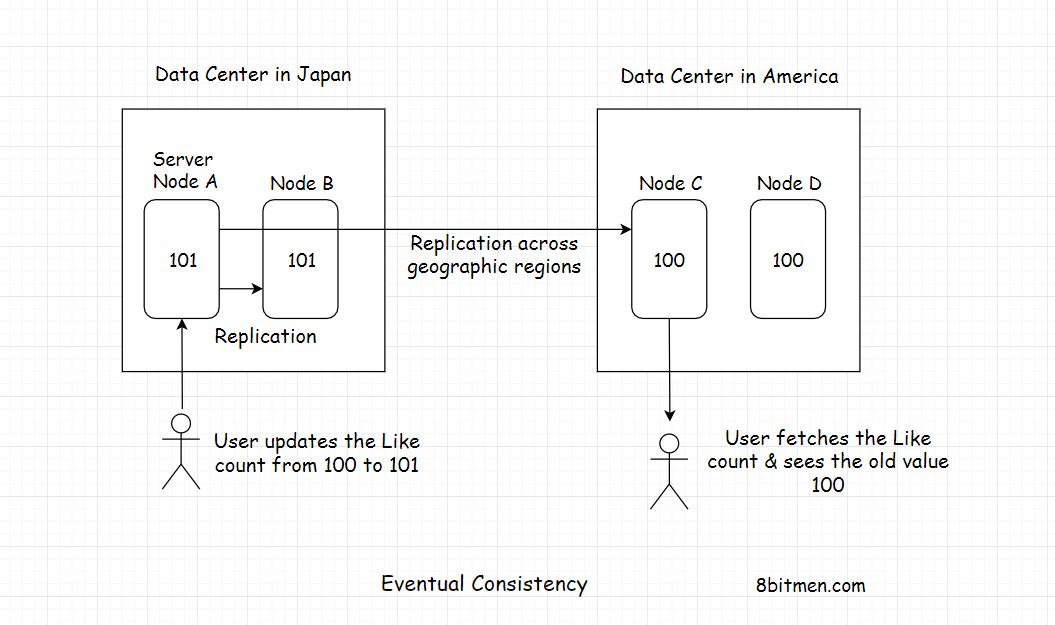
The upside of eventual consistency is that the system can add new nodes on the fly without the need to block any of them, the nodes are available to the end-users to make an update at all times.
Strong consistency
Locking down the nodes needs to be updated.
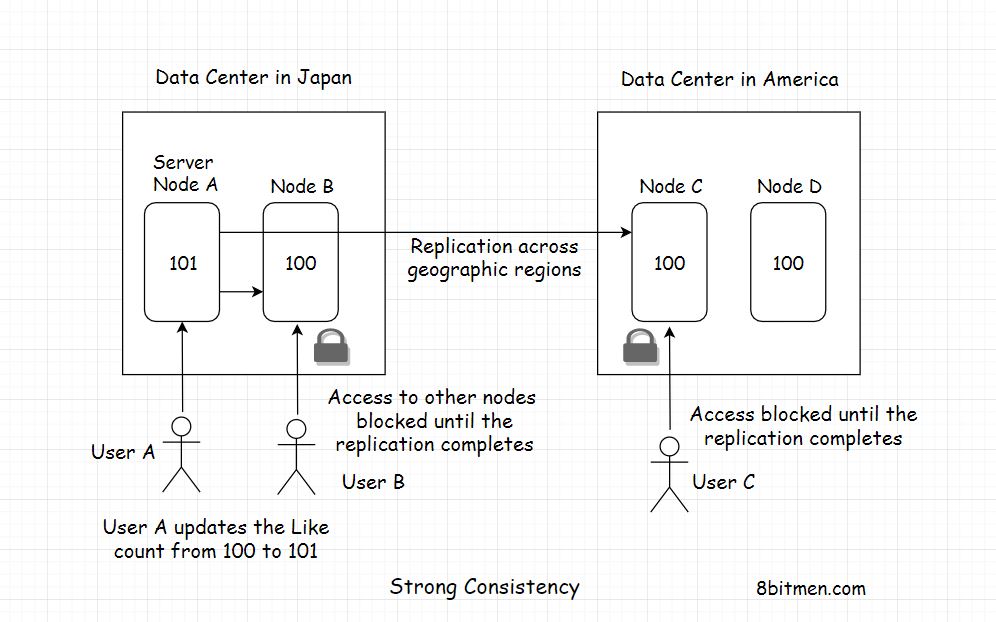
CAP theorem, queuing all the requests.
ACID Trasaction support in the geographic zone.
NoSQL for Highly Available and Scalable.
Consitency, Availability, Partition tolerance(CAP)
CAP theorem simply states that in case of a network failure, when a few of the nodes of the system are down, we have to make a choice between Availability & Consistency
Types of Databases
Document-Oriented database
-
Popular MongoDB, CouchDB, OrientDB, Google Cloud Datastore, Amazon Document DB
-
Use cases
- Real-time feeds
- Live sports apps
- Writing product catalogues
- Inventory management
- Storing user comments
- Web-based multiplayer games
SEGA uses Mongo-DB to improve the experience for millions of mobile gamers
Coinbase scaled from 15k requests per min to 1.2 million requests per minute with MongoDB
Search Engines: Elasticsearch, Splunk, and Solr,
Key-value datastore
minimum latency to implement chaching.
Popular. Redis, Hazelcast, Riak, Voldemort & Memcache.
-
Caching
-
Persisting user state
-
Persisting user sessions
-
Managing real-time data
-
Implementing queues
-
Creating leaderboards in online games & web apps
-
Implementing a pub-sub system
Inovonics uses Redis to drive real-time analytics on millions of sensor data
Microsoft uses Redis to handle the traffic spike on its platforms
Google Cloud uses Memcache to implement caching on their cloud platform
Wide-column database
primarily used to handle massive amounts of data, technically called the Big Data
analytical use cases, ensuring scalability, performance & high availability at the same time.
column-oriented databases wide-column databases store data in a record with a dynamic number of columns. A record can hold billions of columns
Popular: Cassandra*, HBase, Google BigTable, Scylla DB
Netflix uses Cassandra as the backend database for the streaming service
Adobe uses HBase for processing large amounts of data
Relational database
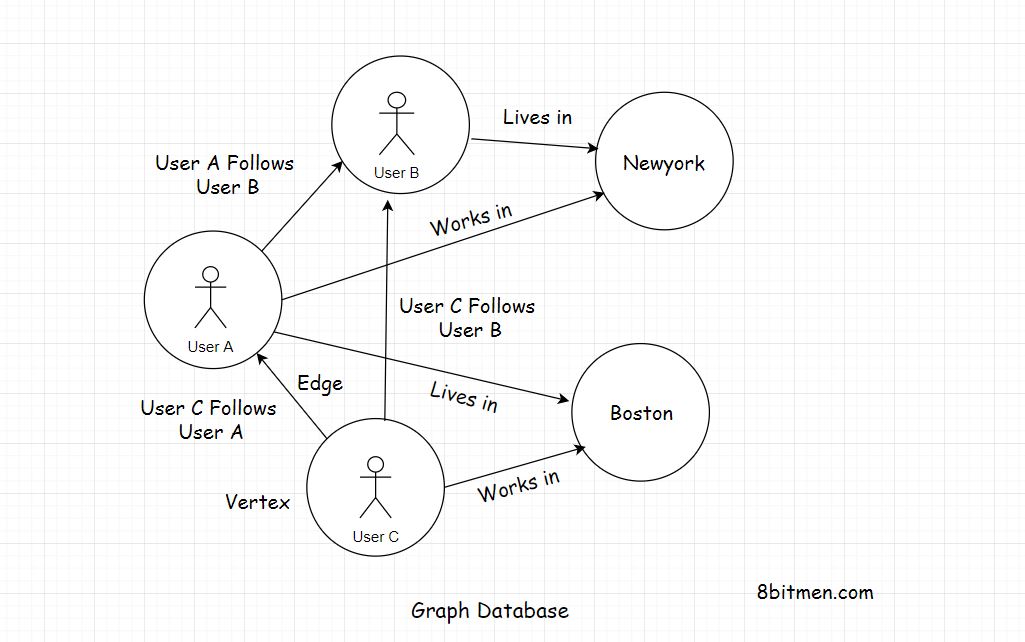
Graph database
Features:
visualization
Low latency: no need to join in SQL, just follow the edges. e.g. Google Maps, Popular . Neo4J*
Use cases: building social, knowledge, network graphs. Writing AI-based apps, recommendation engines, fraud analysis app, storing genetic data etc.
Walmart shows product recommendations to its customers in real-time using Neo4J graph database
Time-Series database
optimized for tracking & persisting time series data
Use cases: data from IoT devices, self-driving vehicles, industry sensors, social networks, stock market financial data
Writing an autonomous trading platform which deals with changing stock prices in real-time etc
fetching data from IoT devices. Managing data for running analytics & monitoring
Primary usage: running analytics, deducing conclusions and making future business decisions looking at the results of the analytics.
Popular : Influx DB*, Timescale DB, Prometheus
IBM uses Influx DB to run analytics for real-time cognitive fraud detection
Spiio uses Influx DB to remotely monitor vertical lining green walls & plant installations.
Databases dedicated to mobile apps
Five of the Most Popular Databases for Mobile Apps - Trigent Vantage