Web app and architecture
Web Application & Software Architecture
Architectural styles:
client-server, peer to peer decentralized architecture, microservices
Overview
architects, developers and product owners study and discuss business requirements (Requirement Gathering & Analysis).
Proof of Concept(POC)
Software Tiers
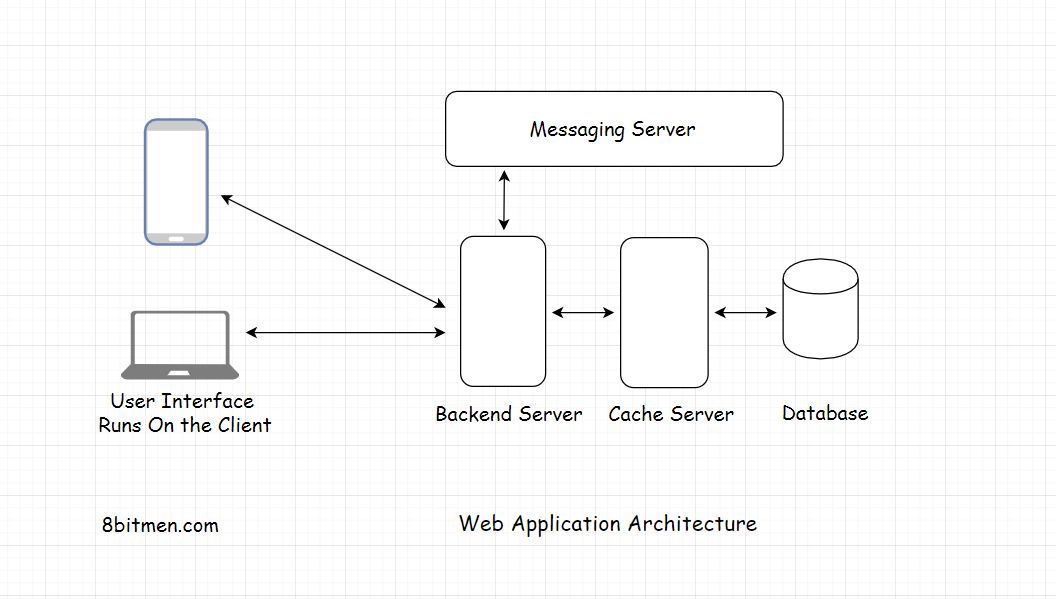
Tiers are logical separation of components in an application or a service. Not just code level, component level like database, UI, backend, message caching.
-
Single-Tier - UI, Backend business logic, DB in the same machine
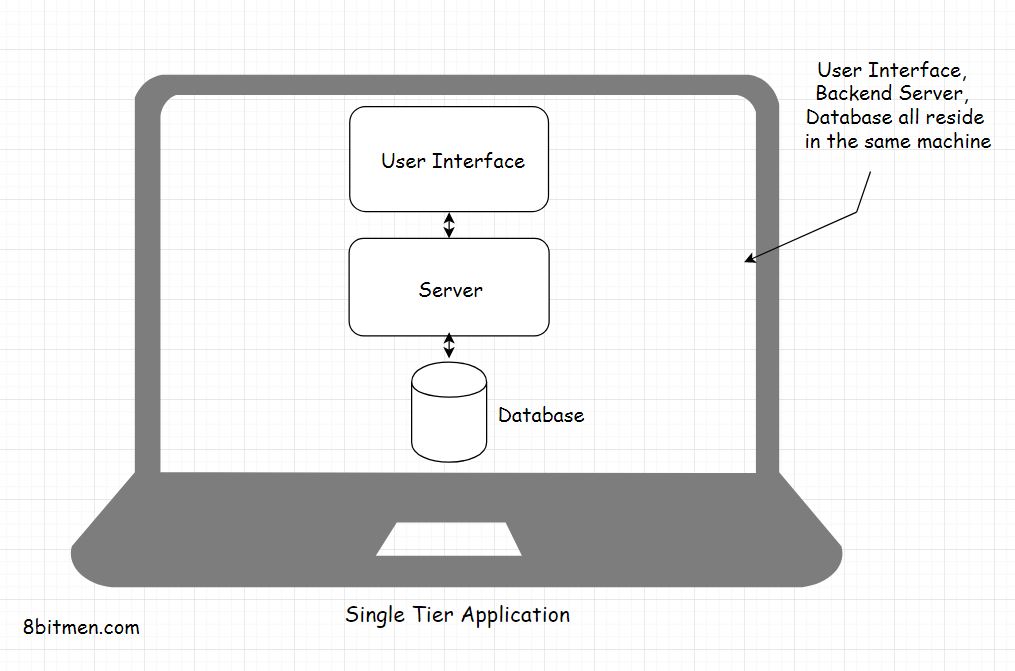 Pros: no latency, data safety
Cons: The business cannot control after software releases.
Pros: no latency, data safety
Cons: The business cannot control after software releases. -
Two-Tier - Client with UI and business logic, backend server includes DB.
 Pros: UI, application logic & DB all in different machines.
Pros: UI, application logic & DB all in different machines. -
Three-Tier - Client with UI,
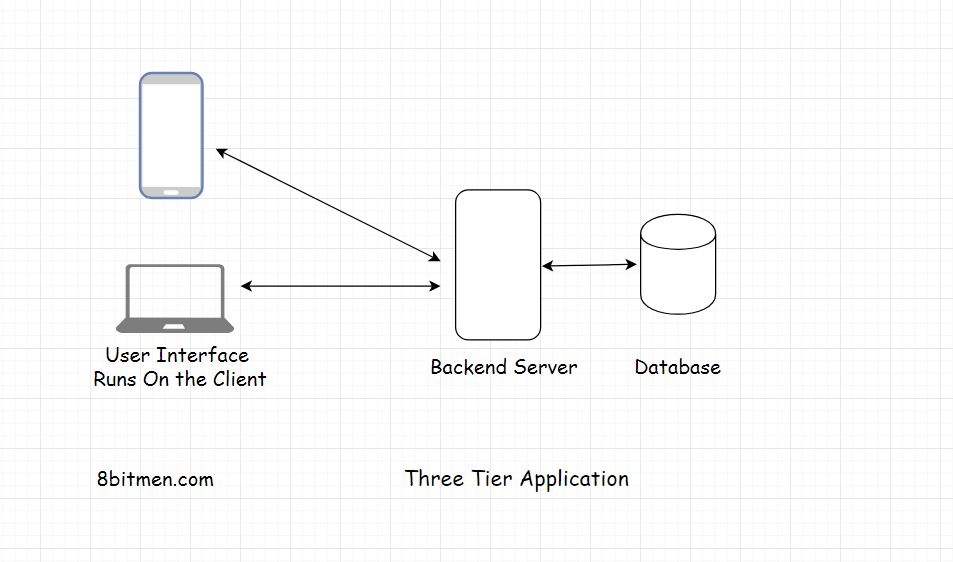
-
N Tier > 3 components. Cache, Message queues for asynchronous behavior, load balancers. search server web microservice.
Layers and Tiers
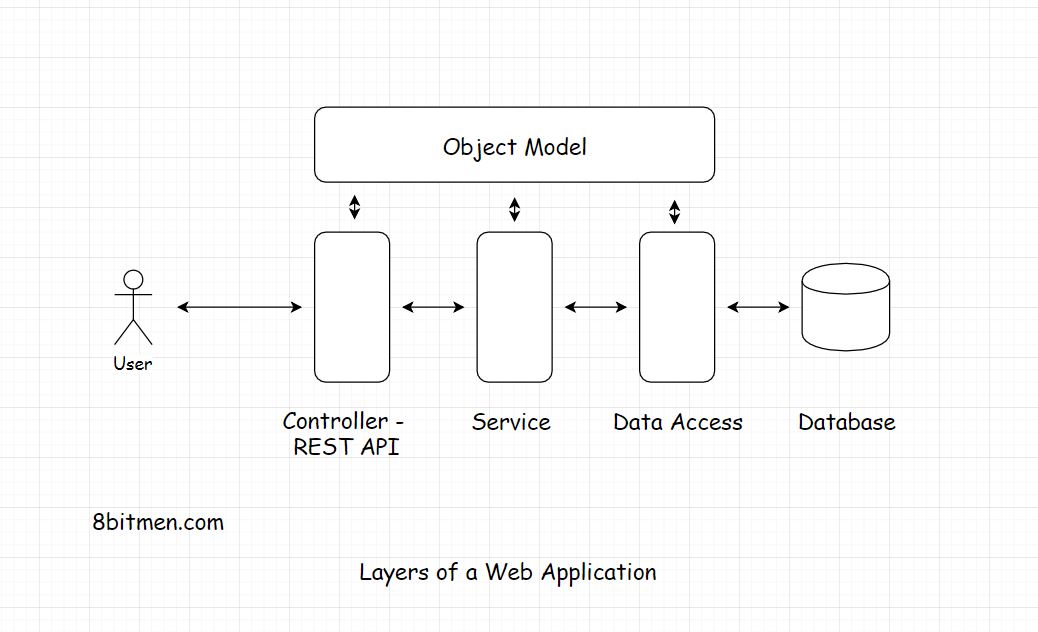
What's web architecture
Multiple components like DB, message queue, cache, UI runs together to form an online service.

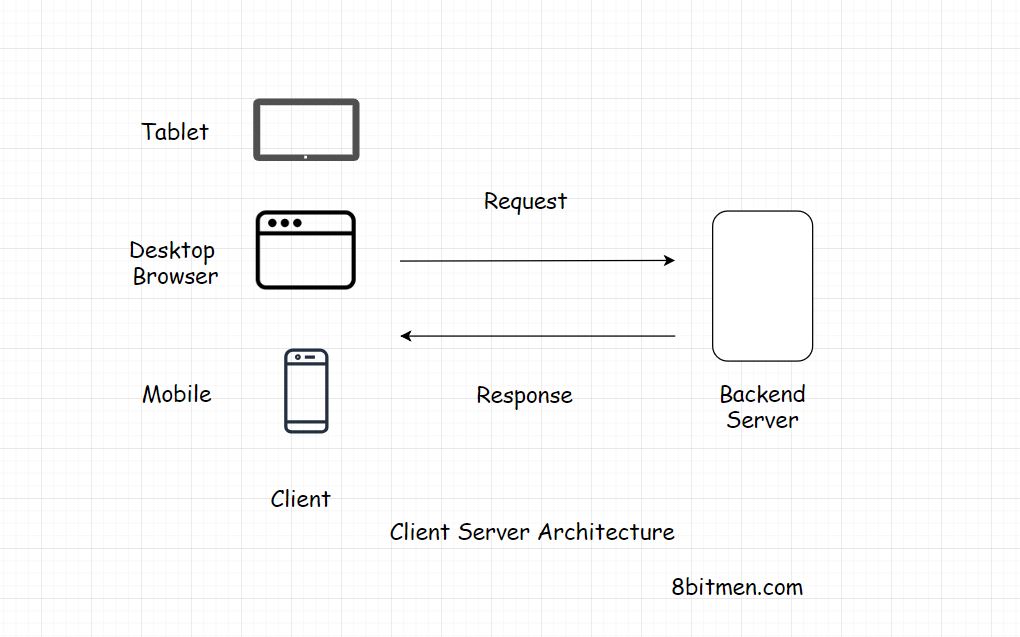
Client Server Architecture(request-response model)
Client: presentation part of the application, HTML, JS, CSS.
open-source technologies popular for writing the web-based user interface are ReactJS, AngularJS, VueJS, Jquery
StackOverflow popular technology
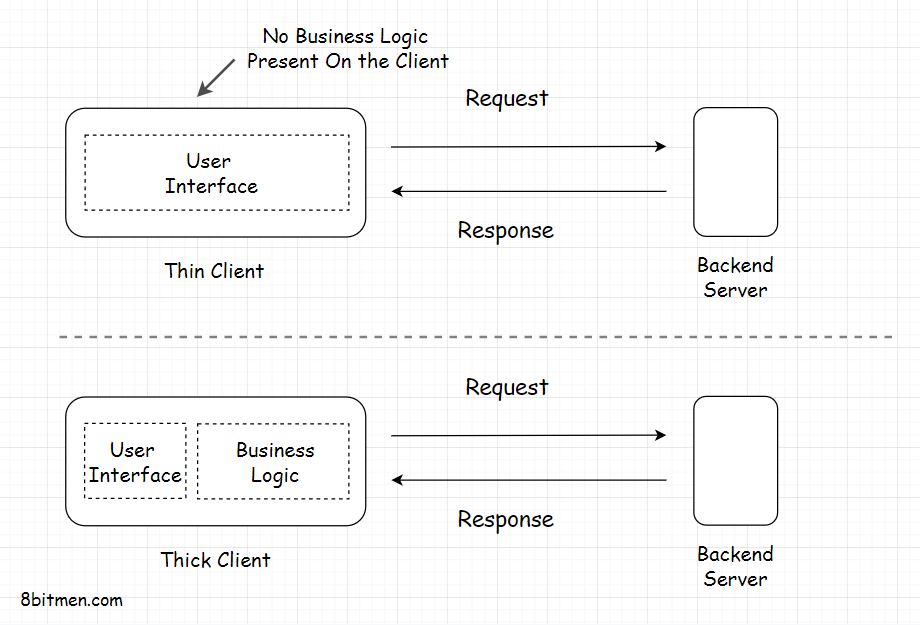
Client
Thin client: just UI. No business logic. Just like a three-tier application. Thick(Fat) client: holds some business logic. Two-tier applications. Utility apps (docker registry), online games.
Server
Web servers means application servers.
Other servers include proxy server, mail server, file server, virtual server.
Server side rendering
Render the UI on the backend and send it to the client.
Communication
Stateless protocol.
REST API
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. It’s a software architectural style for implementing web services. Web services implemented using the REST architectural style are known as the RESTful Web services.
RESTful Web services allow the requesting systems to access and manipulate textual representations of Web resources by using a uniform and predefined set of stateless operations.
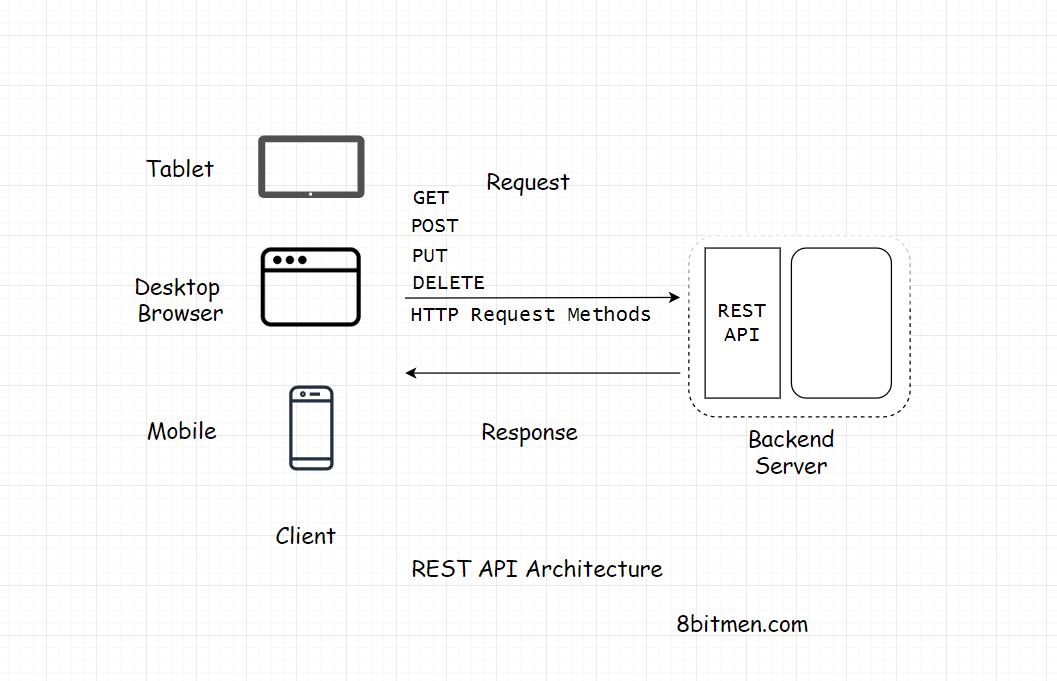
Stateless communication between client and server.
REST Endpoint: url of a service.
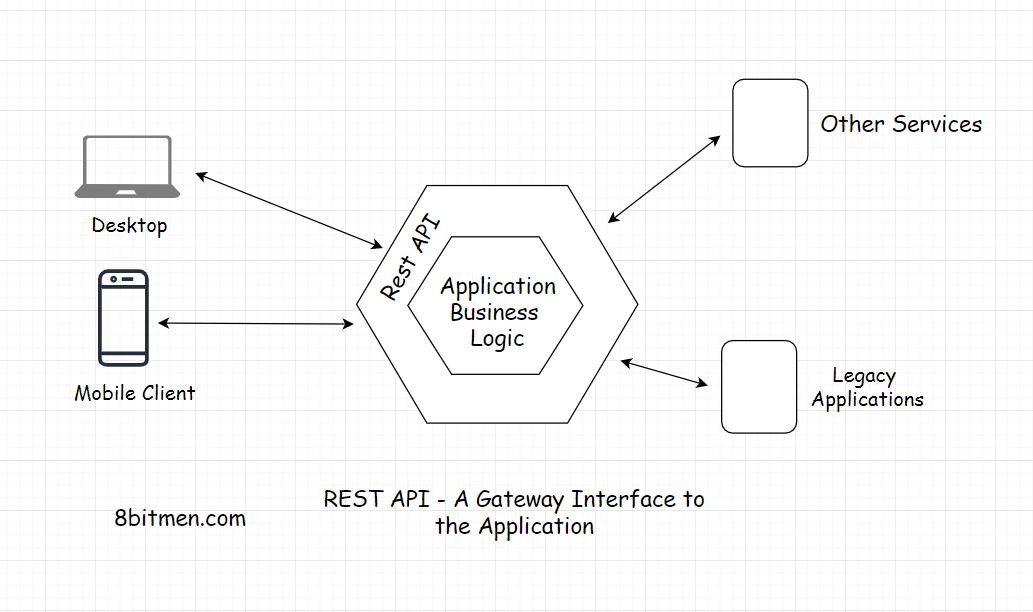
REST-API gateway.
HTTP Push & Pull
Clients use AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript & XML) to send requests to the server in the HTTP Pull based mechanism.
There are multiple technologies involved in the HTTP Push based mechanism such as:
- Ajax Long polling
- Web Sockets
- HTML5 Event Source
- Message Queues
- Streaming over HTTP
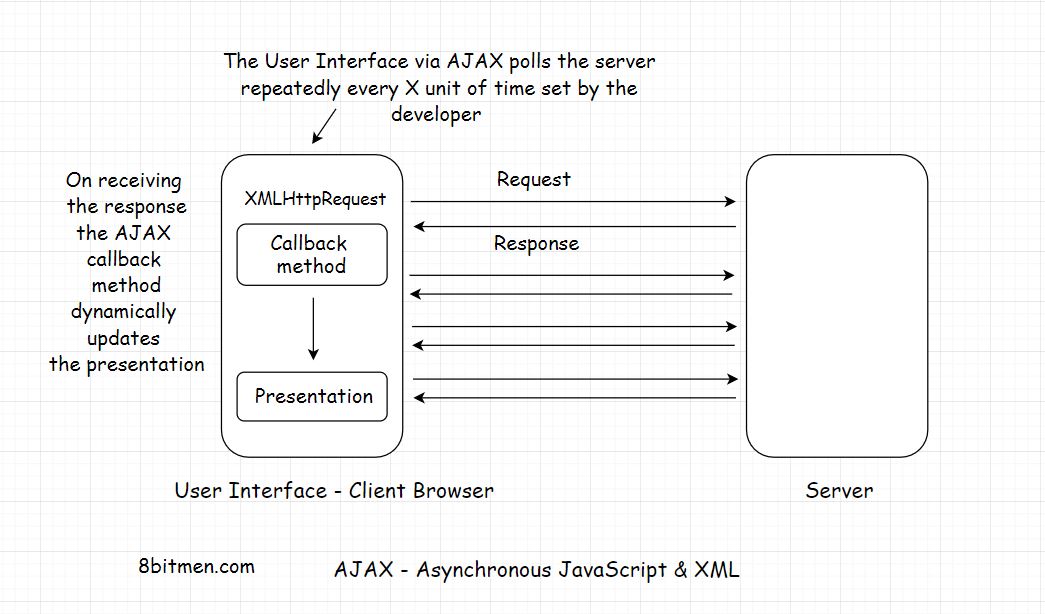
AJAX uses an XMLHttpRequest(XHR) object for sending the requests to the server which is built-in the browser and uses JavaScript to update the HTML DOM
AJAX is commonly used with the Jquery
This dynamic technique of requesting information from the server after regular intervals is known as Polling.
HTTP Pull-Push differences:
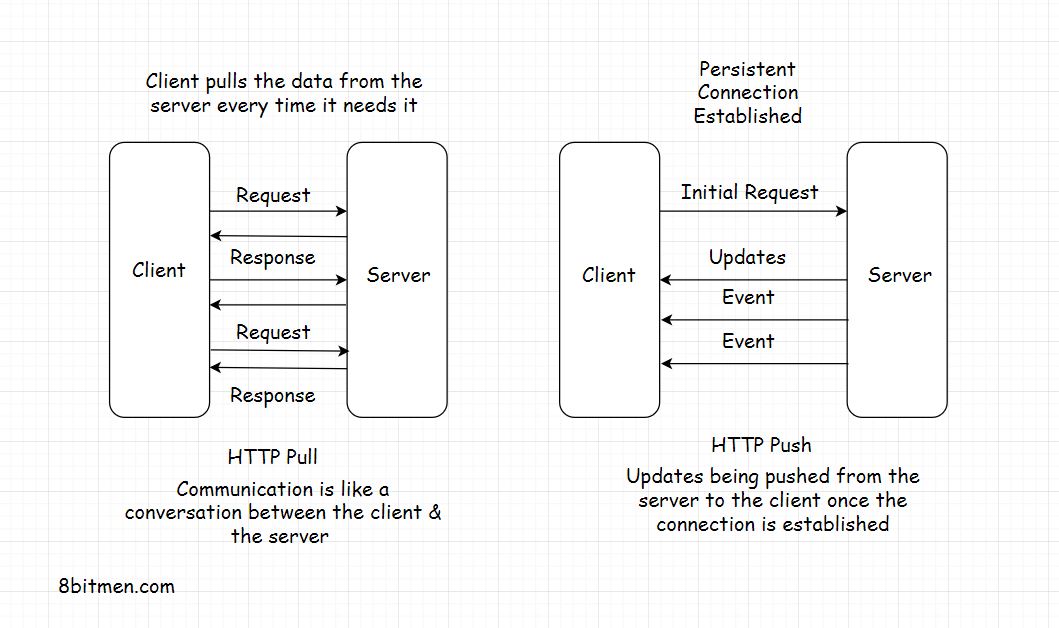
Persistent connection and heartbeat interceptors, which is resource intensive.
Long opened connections can be implemented by multiple techniques such as Ajax Long Polling, Web Sockets, Server-Sent Events etc.
Web sockets - bidirectional data flow
messaging, chat applications, real-time social streams & browser-based massive multiplayer games which have quite a number of read writes in comparison to a regular web app
The WebSocket API & Introducing WebSockets – Bringing Sockets to the Web
Long Polling
lies somewhere between Ajax & Web Sockets. instead of immediately returning the response, the server holds the response until it finds an update to be sent to the client.
HTML5 Event Source API & Server Sent Events(SSE)
Server-sent events - Web APIs | MDN
SSE is ideal for scenarios such as a real-time feed like that of Twitter, displaying stock quotes on the UI, real-time notifications etc.
HTML5 & a JavaScript Stream API
Streams API concepts - Web APIs
Client-Side Vs Server-Side Rendering
We can use server-side rendering for the home page & for the other static content on our website & use client-side rendering for the dynamic pages.